(21) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int a=5;
float b;
printf("%d",sizeof(++a+b));
printf(" %d",a);
}
(a)2 6
(b)4 6
(c)2 5
(d)4 5
(e)Compiler error
Output: (d)
Explanation:
++a +b
=6 + Garbage floating point number
=Garbage floating point number
//From the rule of automatic type conversion
Hence sizeof operator will return 4 because size of float data type in c is 4 byte.
Value of any variable doesn’t modify inside sizeof operator. Hence value of variable a will remain 5.
(23) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
char *str;
scanf("%[^\n]",str);
printf("%s",str);
}
(a)It will accept a word as a string from user.
(b)It will accept a sentence as a string from user.
(c)It will accept a paragraph as a string from user.
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (b)
Explanation:
Task of % [^\t] is to take the stream of characters until it doesn’t receive new line character ‘\t’ i.e. enter button of your keyboard.
(25) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int array[3]={5};
int i;
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
printf("%d ",array[i]);
}
(a)5 garbage garbage
(b)5 0 0
(c)5 null null
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (b)
Explanation:
Storage class of an array which initializes the element of the array at the time of declaration is static. Default initial value of static integer is zero.
(26) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int array[2][2][3]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
printf("%d",array[1][0][2]);
}
(a)4
(b)5
(c)6
(d)7
(e)8
Output: 8
Explanation:
array[1][0][2] means 1*(2*3)+0*(3)+3=9th element of array starting from zero i.e. 8.
(28) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void call(int,int,int);
void main(){
int a=10;
call(a,a++,++a);
}
void call(int x,int y,int z){
printf("%d %d %d",x,y,z);
}
(a)10 10 12
(b)12 11 11
(c)12 12 12
(d)10 11 12
(e)Compiler error
Output: (e)
Explanation:
Default parameter passing scheme of c is cdecl i.e. argument of function will pass from right to left direction.
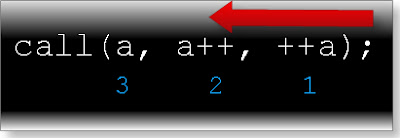
First ++a will pass and a=11
Then a++ will pass and a=11
Then a will pass and a=12
(29) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int x=5,y=10,z=15;
printf("%d %d %d");
}
(a)Garbage Garbage Garbage
(b)5 10 15
(c)15 10 5
(d)Compiler error
(e)Run time error
Output: (c)
Explanation:
Auto variables are stored in stack as shown in following figure.
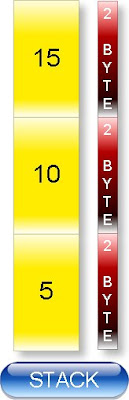
Stack follow LIFO data structure i.e. last come and first out. First %d will print then content of two continuous bytes from the top of the stack and so on.
(30) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
register int i,x;
scanf("%d",&i);
x=++i + ++i + ++i;
printf("%d",x);
}
(a)17
(b)18
(c)21
(d)22
(e)Compiler error
Output: (e)
Explanation:
In c register variable stores in CPU it doesn’t store in RAM. So register variable have not any memory address. So it is illegal to write &a.
(31) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int a=5;
int b=10;
{
int a=2;
a++;
b++;
}
printf("%d %d",a,b);
}
(a)5 10
(b)6 11
(c)5 11
(d)6 10
(e)Compiler error
Output: (c)
Explanation:
Default storage class of local variable is auto. Scope and visibility of auto variable is within the block in which it has declared. In c, if there are two variables of the same name then we can access only local variable. Hence inside the inner block variable a is local variable which has declared and defined inside that block. When control comes out of the inner block local variable a became dead.
(32) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
float f=3.4e39;
printf("%f",f);
}
(a)3.4e39
(b)3.40000…
(c)+INF
(d)Compiler error
(e)Run time error
Output: (c)
Explanation:
If you will assign value beyond the range of float data type to the float variable it will not show any compiler error. It will store infinity.
(33) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
enum color{
RED,GREEN=-20,BLUE,YELLOW
};
enum color x;
x=YELLOW;
printf("%d",x);
}
(a)-22
(b)-18
(c)1
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (b)
Explanation:
Default value of enum constant = value of previous enum constant +1
Default value of first enum constant=0
Hence:
BLUE=GREEN+1=-20+1=-19
YELLOW=BLUE+1=-19+1=-18
(34) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
asm{
mov bx,8;
mov cx,10
add bx,cx;
}
printf("%d",_BX);
}
(a)18
(b)8
(c)0
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (a)
Explanation:
asm keyword is used to write assembly language program in c. mov command stores the constants in the register bx, cx etc. add command stores the content of register and stores in first register i.e. in bx.
(35) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
enum xxx{
a,b,c=32767,d,e
};
printf("%d",b);
}
(a)0
(b)1
(c)32766
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (d)
Explanation:
Size of enum constant is size of sign int. Since value of c=32767. Hence value of d will be 32767+1=32768 which is beyond the range of enum constant.
(36) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
signed int a=-1;
unsigned int b=-1;
if(a==b)
printf("%d %d",a,b);
else
printf("Not equal");
}
(a)-1 -1
(b)-1 32767
(c)-1 -32768
(d)Not equal
(e)Compiler error
Output: (a)
Explanation:
(37) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
float f=5.5f;
float x;
x=f%2;
printf("%f",x);
}
(a)1.500000
(b)1.000000
(c)5.500000
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (d)
Explanation:
(38) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int a=-20;
int b=-3;
printf("%d",a%b);
}
(a)2
(b)-2
(c)18
(d)-18
(e)Compiler error
Output: (b)
Explanation:
Sign of resultant of modular division depends upon only the sign of first operand.
(39) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
char c='0';
printf("%d %d",sizeof(c),sizeof('0'));
}
(a)1 1
(b)2 2
(c)1 2
(d)2 1
(e)None of above
Output: (c)
Explanation:
(40) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
char *url="c:\tc\bin\rw.c";
printf("%s",url);
}
(a)c:\tc\bin\rw.c
(b)c:/tc/bin/rw.c
(c)c: c inw.c
(d)c:cinw.c
(e)w.c in
Output: (e)
Explanation:
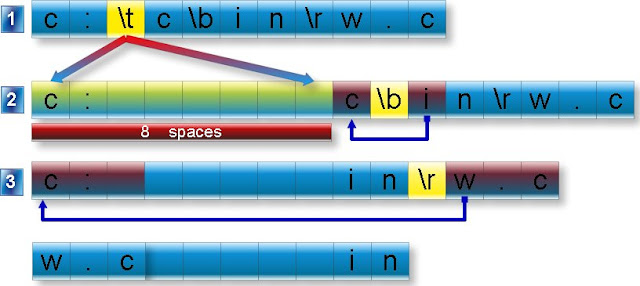
1. \t is tab character which moves the cursor 8 space right.
2. \b is back space character which moves the cursor one space back.
3. \r is carriage return character which moves the cursor beginning of the line.
(41) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
clrscr();
goto abc;
printf("main");
getch();
}
void dispaly(){
abc:
printf("display");
}
(a)main
(b)display
(c)maindisplay
(d)displaymain
(e)Compiler error
Output: (e)
Explanation:
Label of goto cannot be in other function because control cannot move from one function to another function directly otherwise it will show compiler error: unreachable label
(42) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int i=3;
if(3==i)
printf("%d",i<<2<<1);
else
printf("Not equal");
}
(a)1
(b)48
(c)24
(d)Not equal
(e)Compiler error
Output: (c)
Explanation:
Associative of bitwise left shifting operator is left to right. In the following expression:
i<<2<<1
There are two bitwise operators. From rule of associative leftmost operator will execute first.
i <<><<>
After execution of leftmost bitwise left shifting operator:
so i=i*pow(2,2)
=3*
(43) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int x=2,y=3;
if(x+y<=5)
printf("True");
else
printf("False");
}
(a)True
(b)False
(c)Compiler error: Lvalued required
(d)Compiler error: Invalid expression
(e)None of above
Output: (a)
Explanation:
Expression x+y<=5
=> 2+3 <=5
=> 5<=5 is true because 5 is either greater than 5 or equal to 5.
(44) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
const int i=5;
i++;
printf("%d",i);
}
(a)5
(b)6
(c)0
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (d)
Explanation:
We cannot modify the const variable by using increment operator.
(46) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int i=11;
int const * p=&i;
p++;
printf("%d",*p);
}
(a)11
(b) 12
(c)Garbage value
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (c)
Explanation:
In the following line:
int const * p=&i;
*p i.e. content of p is constant pointer p is not constant pointer. So we can modify the pointer p. After incrementing the pointer it will point next memory location and its content will any garbage value.
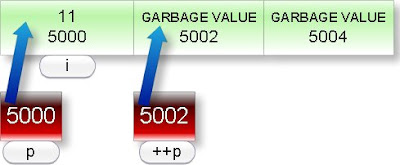
Note: We have assumed arbitrary memory address.
To make pointer p as constant pointer write:
int const * const p=&i;
(47) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int a=15,b=10,c=5;
if(a>b>c )
printf("Trre");
else
printf("False");
}
(a)True
(b)False
(c)Run time error
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (b)
Explanation:
Relation operator in c always returns 1 when condition is true and 0 when condition is false. So in the following expression
a > b > c
Associative of relational operators are left to right order of execution will be following manner:

Hence in this expression first solve bolded condition: a > b > c
Since condition a>b is true so result will be 1. Now expression became:
1 > c
Since this condition is false so result will be 0. Thus else part will execute.
(48) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
float f;
f=3/2;
printf("%f",f);
}
(a)1.5
(b)1.500000
(c)1.000000
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (b)
Explanation:
In the following expression:
f=3/2 both 3 and 2 are integer constant hence its result will also be an integer constant i.e. 1.
(49) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
void main(){
int a=sizeof(a);
a=modify(a);
printf("%d",a);
}
int modify(int x){
int y=3;
_AX=x+y;
return;
}
(a)2
(b)3
(c)5
(d)Garbage value
(e)None of above
Output: (c)
Explanation:
_AX is register pseudo variable. It stores return type of function.
(50) What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
#define PRINT printf("c");printf("c++");
void main(){
float a=5.5;
if(a==5.5)
PRINT
else
printf("Not equal");
}
(a)c c++
(b)Not equal
(c)c
c++
(d)Compiler error
(e)None of above
Output: (d)
Explanation:
First see intermediate file:
try.c 1:
try.c 2: void main(){
try.c 3: float a=5.5;
try.c 4: if(a==5.5)
try.c 5: printf("c");printf("c++");
try.c 6: else
try.c 7: printf("Not equal");
try.c 8: }
try.c 9:
try.c 10:
If there are more than one statement in if block then it is necessary to write inside the { } otherwise it will show compiler error: misplaced else
via http://cquestionbank.blogspot.com
via http://cquestionbank.blogspot.com
No comments:
Post a Comment